The Evolution of Manufacturing: A Journey through Industrial Revolutions
The history of manufacturing is a captivating tale of progress and innovation, with each industrial revolution bringing about significant changes in production methods and technologies. These revolutions have revolutionized the way goods are produced, increasing efficiency, productivity, and improving the quality of life. Let’s take a closer look at the four distinct industrial revolutions that have shaped the manufacturing landscape.
The First Industrial Revolution (Late 18th to Early 19th Century)

The First Industrial Revolution marked a pivotal shift from manual production methods to machine-based manufacturing. Steam power and water power played a crucial role in this revolution, enabling the introduction of mechanical looms and the steam engine. Industries like iron and textiles thrived during this period, transforming agrarian societies into industrial hubs. The factory system emerged, bringing about significant socio-economic and cultural changes.
The Second Industrial Revolution (Late 19th to Early 20th Century)

The Second Industrial Revolution witnessed the advent of mass production and assembly line manufacturing, powered by electricity. This revolution saw the widespread use of electrical power and the invention of the internal combustion engine. Advancements in chemical, petroleum, and steel production further fueled this revolution. Mass production made goods more accessible to the general population, driving significant economic growth and urbanization.
The Third Industrial Revolution (Late 20th Century)

The Third Industrial Revolution introduced automation to manufacturing processes through electronics and information technology. The development of computers, robotics, and the early stages of digitalization revolutionized the manufacturing landscape. This revolution brought about more precise and efficient production, reducing human labor in dangerous or repetitive tasks. The concept of flexible manufacturing systems was also introduced.
Manufacturing 4.0 (21st Century)
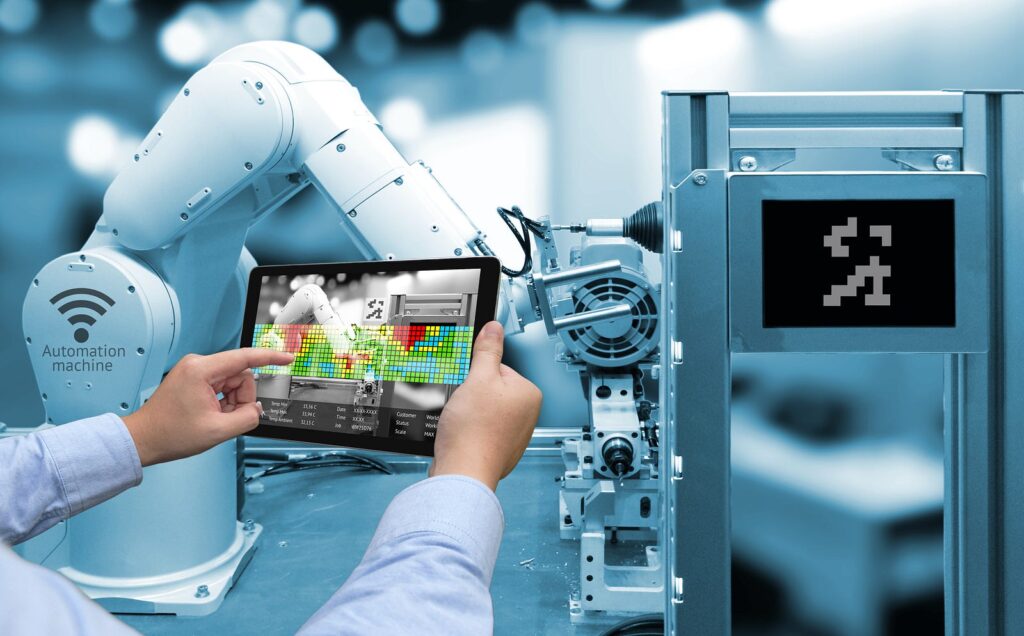
Manufacturing 4.0 represents the current frontier of manufacturing, characterized by the digital transformation of production processes. This revolution integrates cyber-physical systems, the Internet of Things (IoT), and artificial intelligence. Advanced data analytics, AI and machine learning, robotics, additive manufacturing (3D printing), and big data analytics for predictive insights are key technological innovations driving Manufacturing 4.0.
Manufacturing 4.0 brings about highly efficient, flexible, and customizable production processes. It enables manufacturers to respond swiftly to market demands and introduces the concept of smart factories. This revolution emphasizes not just automation but also intelligence, adaptability, and integration across global networks.
Each industrial revolution has paved the way for the next, building upon the technological advancements and societal changes of its predecessor. Manufacturing 4.0 represents the culmination of centuries of progress, reflecting humanity’s unwavering pursuit of efficiency, quality, and sustainability in the production of goods. It has shaped economies, transformed lives, and continues to push the boundaries of what is possible in manufacturing.
